
A research team led by Prof. HUANG Xingjiu from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences constructed a highly stable solid contact calcium ion-selective electrode. They used synchrotron radiation technique to reveal the transduction mechanism by which the solid contact layer participated in the potential response.
The results were published in Analytical Chemistry.
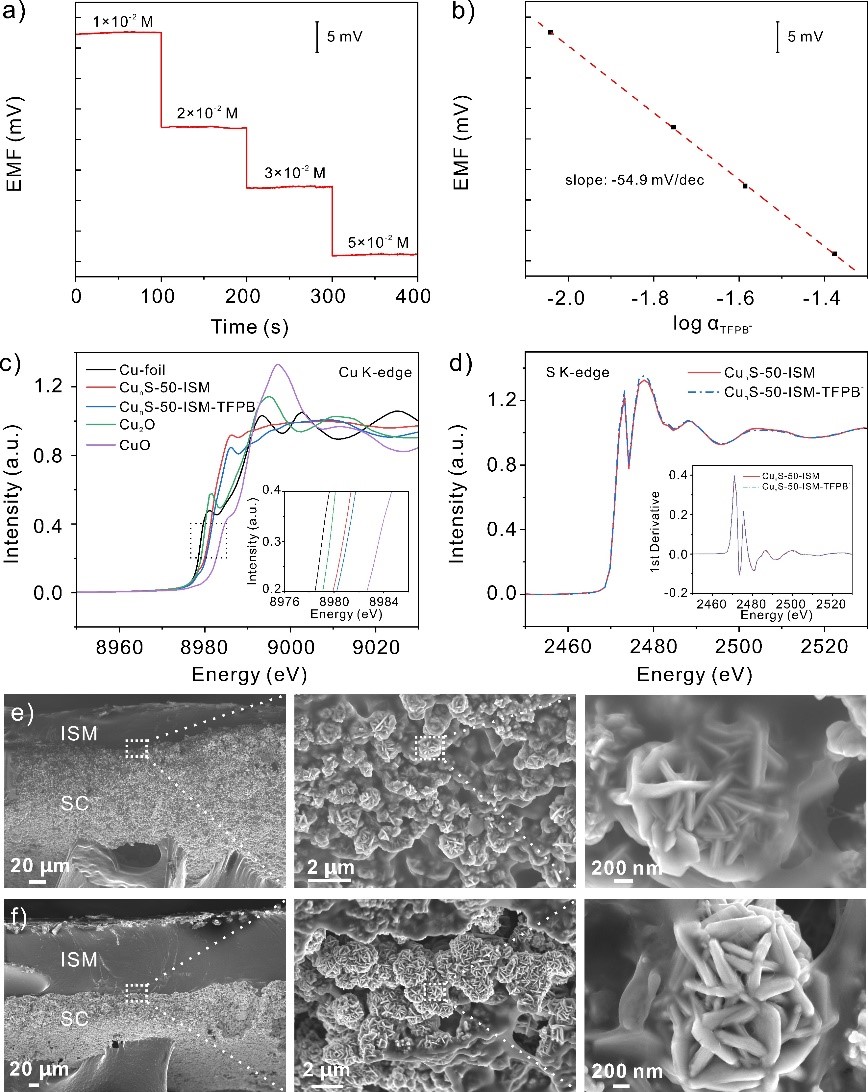
Solid contact (SC) ion-selective electrodes (ISEs) are widely used in environmental monitoring and biomedical fields due to their fast response and high sensitivity. Stability is an important criterion in evaluating the performance of SC-ISEs. The capacitance and hydrophobicity of SC materials affect the potential stability. Therefore, researchers have focused on designing SC materials with large capacitance and high hydrophobicity and exploring the corresponding transduction mechanism.
In this work, a special sensor SC-ISEs was developed using copper sulfide (CunS-50) nanoflowers. It's with large capacitance anfd high hydrophobicity. Also, the sensor can accurately and reliably detect calcium ions (Ca2+).
The copper sulfide nanoflowers were synthesized by modification with surfactant. This modification not only made the nanoflowers more water repellent, but also enhanced their ability to store and release electrical charge.
The researchers also explained the transduction mechanism. The lipophilic anion participated in the redox reaction of Cu+/Cu2+ and promoted the generation of free electrons during the potentiometric response.
This work provides a deeper understanding of the transduction mechanism behind the potentiometric response and offers a new idea for the design of redox materials.

Supplementary Cover Image. (Image by LIU Zihao)
The transduction mechanism of CunS-50 participating in potentiometric response. (Image by LIU Zihao)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

